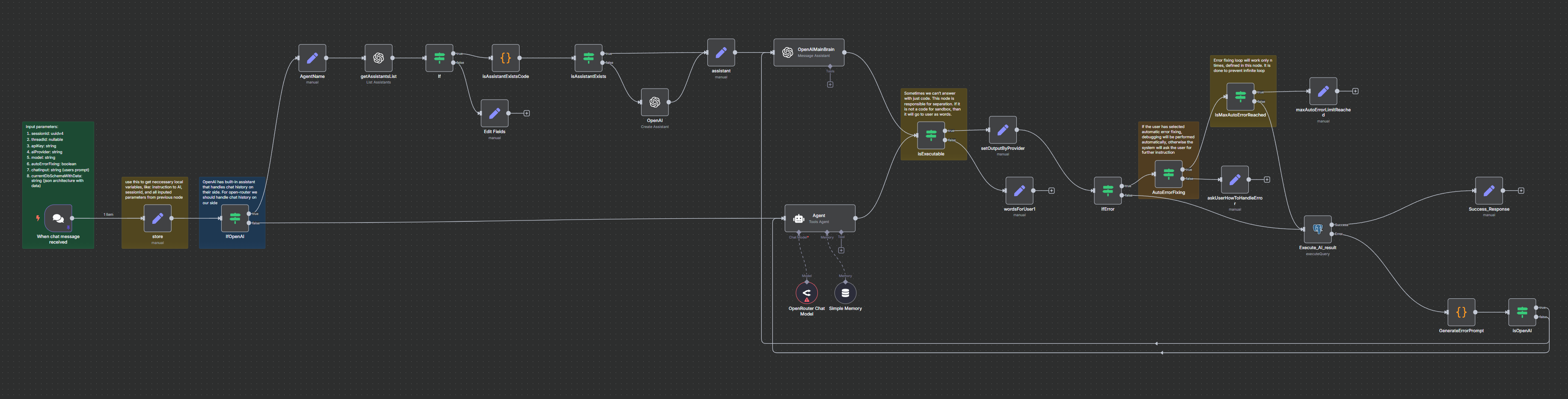
It generated SQL query and finished in 3 attempts (see the bottom of the image). It means it generated 1st query to solve your task, run it in a sandbox, get error, fixed, get another error, fixed again and finally got the SQL query that works and returned the Execution result.
You can see how it worked step by step. By comparing "Execution result" with "Your current db tables" you can double-check if it performs as expected. We have plans to automate and help user to double-check. For more details please visit Roadmap page.
And as you can see this method isolates the task and uses only required tables and columns. This was the main purpose of using the sandbox.
Tip: If you didn't get the result you expected (in "current db tables", in mock schema generation, in "Execution result"), spent 2-3 mins to understand, if you see that it differs a lot, just start New Chat and ask again the same prompt.
Another Tip: If you will give a super complex task, even with 50 New chat itterations you can not get the expected result. In this case please decompose task into smaller parts by yourself and give each part separately to isra36. It will require you to build entire final query by yourself, but it will be much faster and you will be sure that each part is working as expected. To understand is it complex or not, just try 3,4 New chat iterations and see if it works.
Instead of Scientific results
We have tested the `How to check if all {pattern}_id foreign columns have indexes or not through all tables` complex prompt with gpt-4.1-nano and it was performed successfully in 2 iterations (with 1 error). That means this technique can be used to generate working SQL queries even with small models. But of course isra36 in production uses more complex model. Currently it is gpt-4.1.